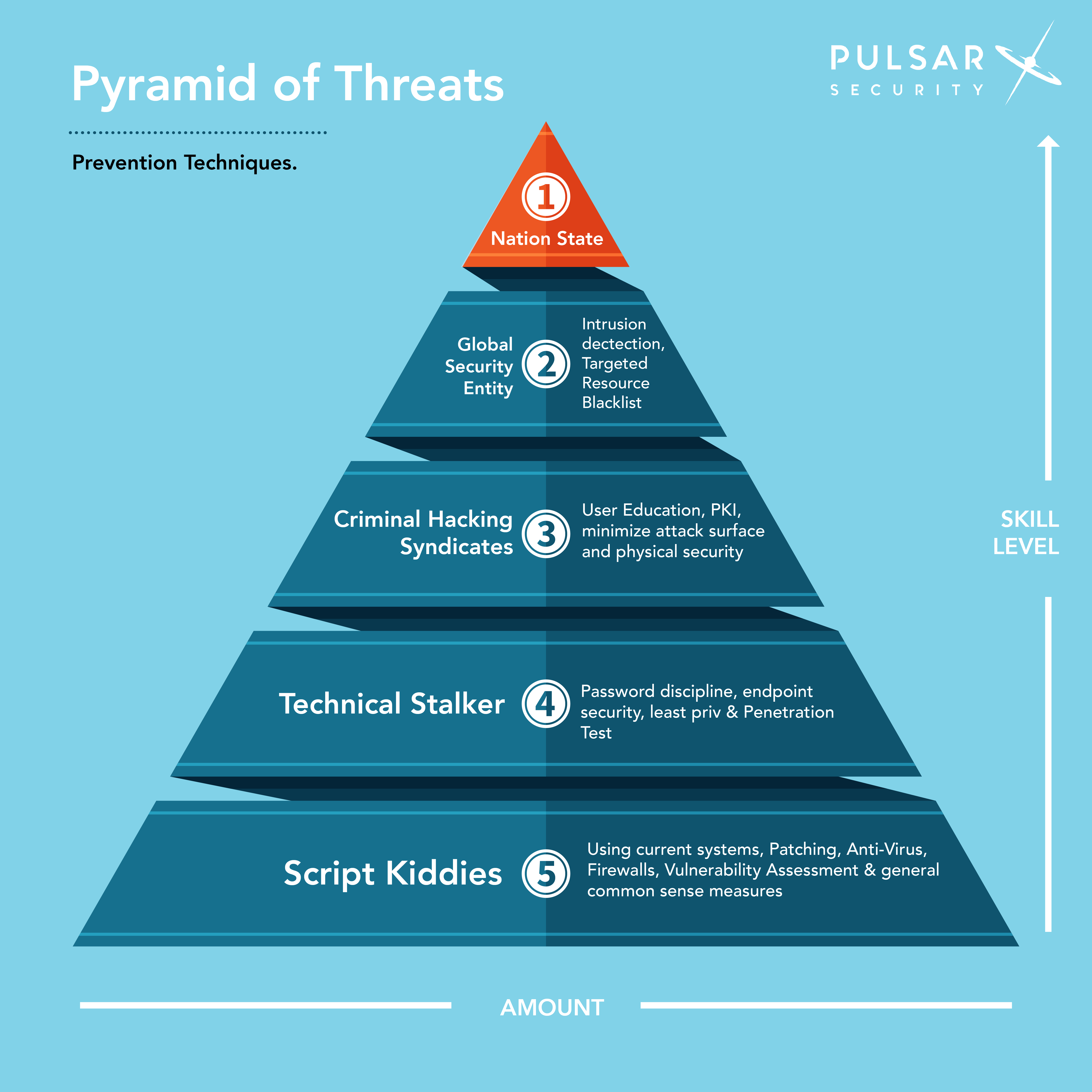
Pyramid of Threats | Prevention of Threats to the Enterprise
This is part 2 of our two-series article that focuses on Pulsar Security’s Pyramid of Threats, detailing types of cyber threats, their level of skills, how commonly they occur, and ways to prevent them. The first piece highlights how cyberspace has become a war frontier for nation-states, associated proxies, organized cybercrime groups, technical stalkers, and other malicious actors seeking to gain the upper hand. Simply put, there are far too many threat sources out there to ignore the risks. Next, this article covers prevention measures on ways to safeguard businesses effectively from the identified threats.
How To Prevent Nation-State Threats
1. Avoid Acquiring Technological Products from Adversarial Nations
Countries like Russia, China, North Korea, and Iran lead the pack when it comes to nation-state threats and attacks. In this regard, cybersecurity standards, such as NIST SP 800-53 Revision 4, have issues d guidelines and controls that restrict the purchase of technological infrastructures from specific vendors and countries. For example, one of the controls prohibits the US federal agencies from purchasing equipment or components from two Chinese organizations, ZTE and Huawei. Essentially, government and private entities should avoid buying IT equipment from countries that pose a threat. Caution and acknowledging risks are crucial practices in mitigating possible attacks from nation-states.
2. Isolate Corporate Networks from the Internet
One of the safest methods for protecting valuable data from nation-state threats is completely isolating corporate networks and internal systems from the internet. For instance, companies can use low-cost demilitarized zones (DMZ) to separate and shield internal networks from the online world. In particular, government entities and private multinationals should isolate internet access optimally by physically isolating internal networks using one-way, secured paths to move sensitive information from internal networks. While this may pose challenges for enterprises that have integrated their corporate networks to the internet, they should adopt the notion that they may become data breach victims and implement data loss prevention and encryption technologies to bolster defenses.
3. Cyberthreat Intelligence Sharing
Sharing cyberthreat intelligence between government organizations and private entities can assist in preventing nation-state attacks from adversarial countries. Sharing threat intelligence and crucial security information helps enhance situational awareness. Cybersecurity teams and government cyber teams should coordinate monitoring efforts of the cyber threat landscape to identify attack patterns and threat trends. In addition, government agencies should collaborate with various industry institutions to ensure continuous threat intelligence, which is crucial to preventing threats from foreign adversaries.
How To Prevent Threats From Global Security Entities
1. Intrusion Detection
Global entities use digital mercenaries to execute attacks or steal information on behalf of clients like rogue nations and rival companies. Organizations can protect themselves from these threats by implementing advanced intrusion detection systems. An intrusion detection system applies reactive controls to detect attacks and mitigate them appropriately. For example, an intrusion detection system may monitor network behaviors to identify anomalous events and prevent them from accessing the network. However, since it is a reactive approach, companies should also deploy intrusion detection systems that use a proactive approach to filter harmful traffic from accessing internal networks.
2. Targeted Resource Blacklist
Organizations should develop and continuously update a targeted resource blacklist to define specific entities, IP addresses, or users that should be denied access to internal networks. A targeted resource blacklist comprises suspected entities or those known to be malicious from accessing a system or network. For example, a targeted resource blacklist may consist of specific organizations, email addresses, processes, IP addresses, users, applications, domains, among others. Maintaining a targeted resource blacklist is an effective practice used to protect against threats from global entities since organizations can apply it in all network aspects. Besides, a targeted resource blacklist is threat-centric to ensure that threats cannot enter a network.
How to Prevent Threats From Criminal Hacking Syndicates
1. User Education
Criminal hacking syndicates execute attacks for monetary gains. As a result, they often target weak links in an organization to gain a foothold on internal networks and sensitive information like login credentials for bank and financial accounts. They use techniques like Business Email Compromise and targeted spear-phishing campaigns. Therefore, user education on the best security practices can help prevent threats from criminal hacking syndicates. Educating employees on current dangers and how to avoid them is a critical measure that can enhance a company’s cybersecurity posture.
2. Public Key Infrastructure
Implementing a public key infrastructure provides an organization with a cybersecurity and encryption framework for securing communications between users and servers. With most companies relying on digital technologies to share sensitive information and communicate with clients and supply chains, PKI is vital for building trust and securing a business ecosystem. Specifically, PKI infrastructures provide the ability to verify user and machine identities, thus maintaining the integrity of various transactions and preventing criminal hacking syndicates from gaining unauthorized access.
3. Reducing the Attack Surface
Internet-facing applications, networks, and devices enable a modern business environment to compete effectively and leverage the latest innovations in essential business operations. But, on the other hand, they result in an increased attack surface that permits criminal hacking syndicates to compromise mission-critical services. That said, managing and reducing the attack surface can protect organizations from organized cybercrime groups and threats. Essentially, this involves acquiring full visibility of all endpoints accessing a network, monitoring them continuously to detect malicious activities, and preventing threats in real-time. Managed security service providers are the perfect partners that help companies reduce and manage their attack services to ensure proactive protection from criminal hacking syndicates.
4. Physical Security
Physical security entails implementing measures that restrict access to critical on-premise infrastructure. Also, physical security protects networks, data, hardware, and software from adverse events that may cause damage, data breaches, and attacks. For example, access control mechanisms can prevent users from connecting unknown flash drives that may contain malware. Criminal hacking syndicates may bait employees by leaving malware-infested flash drives within an organization to tempt them into connecting them to company devices and launch an attack remotely.
Preventing Threats From Technical Stalkers
1. Password Discipline
Technical stalkers often target their victims to settle grudges or get revenge. In a workplace, some employees may stalk other employees to cause harm or use their work accounts to steal data from a company. In this case, all employees should practice strong password practices and discipline. Password discipline involves protecting all devices and accounts with strong passwords. Each password should have an adequate length consisting of special characters, uppercase and lowercase alphabetical letters, and numbers. More importantly, users must change their passwords frequently and use password managers to securely generate and store robust passwords.
2. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security can prevent threats from technical stalkers by securing all possible entry points into a network or system. Organizations should employ a defense-in-depth approach to protect mobile devices, IoT deployments, laptops, and desktops from malicious actors. Antivirus solutions, access control mechanisms, endpoint encryption technologies, sandboxing, and securing email gateways can secure all endpoints. Moreover, endpoint detection and response solutions protect endpoints proactively by monitoring them for unusual activities and deploying mitigation measures in real-time.
3. Least Privileged Access Controls
A company should only provide employees with the least access to critical data and systems to prevent threats from technical stalkers. The least privileged access controls give users the freedom to accomplish their tasks by restricting access to resources needed to discharge their responsibilities. Therefore, applying least privilege access to users implies enforcing restricted user rights and the lowest clearance level to ensure that all users complete their duties. As a result, the model prevents technical stalkers with malicious intents from accessing or exfiltrating confidential information.
4. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing processes assist companies in identifying possible ways through which malicious actors can penetrate and compromise their networks and systems. Penetration testers use a hacker’s mindsets and tools to detect and mitigate possible entry points and detected security weaknesses. Hence, it helps seal cybersecurity loopholes that enable technical stalkers to wreak havoc.
How to Prevent Threats From Script Kiddies
1. Using Current Systems
Script kiddies lack the knowledge to develop sophisticated malware or hacking tools and therefore use off-the-shelve tools. However, they can still cause extensive damage to a company’s systems. Therefore, organizations need to use current and updated systems and applications with sufficient security measures to protect against attempted hacks.
2. Patching
New vulnerabilities emerge daily, and script kiddies may try to exploit them to test their prowess. Thus, organizations should implement an automated patching system that identifies systems and applications lacking current security patches and patch them appropriately. Patching systems installs the latest security updates to mitigate emerging vulnerabilities and deter script kiddies from exploiting them.
3. Defense-in-Depth
A defense-in-depth strategy of antivirus solutions, firewalls, and antimalware applications is a critical requirement for all organizations. The solutions protect a network from malware attacks, SQL injections, and other types of attacks that can lead to data loss and malicious intrusions.
4. Vulnerability Assessments
A vulnerability assessment is a process through which an organization systematically reviews cybersecurity flaws and vulnerabilities in a system. The techniques assist in evaluating devices, applications, and systems that are susceptible to attacks to inform the necessary remediation measures. Mitigating identified vulnerabilities can prevent script kiddies from launching and executing attacks.
5. General Common Sense
Today, everyone in an organization uses mobile devices, laptops, and other internet-enabled devices to access various websites and online platforms. Thus, companies must nurture a culture where everyone is security-conscious and understands the required cybersecurity practices. Implementing frequent cybersecurity awareness and training programs can equip everyone with the requisite knowledge to protect against breaches and attacks.

Jill Stagner
Jill is the Director of Marketing and Program Development. She manages the marketing, communication and company branding efforts for Pulsar. In addition, she helps with the public facing materials for all of Pulsar’s products and services.